Sex hormones are hormones that play a role in the development and maintenance of the male and female reproductive systems, as well as secondary sexual characteristics. There are two main categories of sex hormones: androgens and estrogens.
Androgens are responsible for the development and maintenance of male characteristics. The main androgen in males is testosterone, which is produced by the testes. In females, androgens are produced in smaller amounts by the ovaries and the adrenal glands.
Estrogens are responsible for the development and maintenance of female characteristics. The main estrogen in females is estradiol, which is produced by the ovaries. In males, estrogens are produced in smaller amounts by the testes and the adrenal glands.
Sex hormones play a variety of roles in the body. In males, androgens are involved in the development of male secondary sexual characteristics such as facial hair, a deeper voice, and a more muscular build. They also play a role in maintaining muscle mass, bone density, and sex drive. In females, estrogens are involved in the development of female secondary sexual characteristics such as breast development and the menstrual cycle. They also play a role in maintaining bone density and regulating the menstrual cycle.
“Both androgens and estrogens are important for overall health and well-being in both males and females. Imbalances in sex hormone levels can cause a variety of health problems including infertility, osteoporosis, and certain types of cancer.”
Sex hormones, including androgens and estrogens, can affect the brain in many ways. They can influence brain development and function, as well as behavior and mood.
During brain development, sex hormones play a role in the differentiation of the brain into male and female forms. They can also influence the development and organization of neural pathways and networks, and the development of certain brain structures, such as the hippocampus and the amygdala (Figure 1).
In adulthood, sex hormones can continue to influence brain function, including cognition, emotion, and behavior. For example, studies have shown that androgens and estrogens can affect memory, learning, and spatial ability. They can also influence mood and behavior, with some research suggesting that they may be involved in the development of mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety.
The effects of sex hormones on the brain can be complex and depend on a variety of factors, including the timing of exposure, the levels of hormones present, and the presence of other hormones and neurotransmitters. Further research is needed to fully understand the ways in which sex hormones affect the brain.
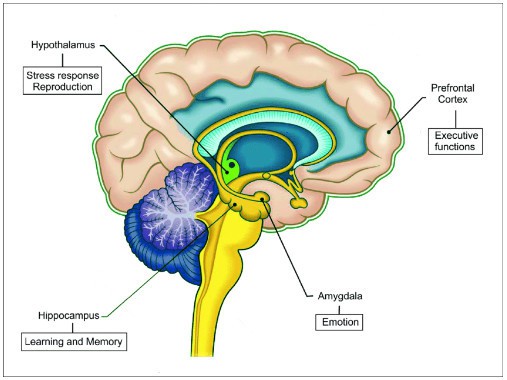
Estrogens, a group of female sex hormones, play a role in shaping brain development in both males and females. During fetal development, estrogens can influence the development and organization of neural pathways and networks, and the development of certain brain structures, such as the hippocampus and the amygdala.
In males, estrogens are produced in smaller amounts than in females, but they are still important for brain development.
For Example
Research has shown that estrogens can affect the development of the corpus callosum, a bundle of nerve fibers that connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain. They may also play a role in the development of the prefrontal cortex, a region of the brain involved in higher cognitive functions such as decision making and problem solving.

In females, estrogens are produced in higher levels, and they play a more significant role in shaping brain development. During puberty, the onset of estrogen production is associated with changes in brain structure and function, including the development of female secondary sexual characteristics, such as breast development and the onset of the menstrual cycle.
Overall, estrogens play a complex and multifaceted role in shaping brain development in both males and females. Further research is needed to fully understand the ways in which estrogens influence brain development and function.
Testosterone is a hormone that is produced by the testes in men and the ovaries in women. It is responsible for the development of male characteristics, such as facial hair, a deep voice, and a muscular build. It is also involved in the production of sperm and the maintenance of bone density and muscle mass.
Testosterone can affect the nervous system in many ways.
For Example
It can influence brain development and function, including the development of neurons and the connections between them. Testosterone has also been shown to affect behavior, mood, and cognition.
Research has suggested that testosterone may have a protective effect on the brain, as low levels of testosterone have been associated with an increased risk of cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. On the other hand, high levels of testosterone have been linked to aggression and risky behavior.
The effects of testosterone on the nervous system are complex and depend on various factors, including an individual’s age, genetics, and overall health. It is important to note that testosterone levels can be affected by various medical conditions and lifestyle factors, and it is important to speak with a healthcare provider if you have any concerns about your testosterone levels.
Sex hormones, such as estrogen and progesterone, play a crucial role in the reproductive process and can also have important effects on a woman’s body and mind during pregnancy and motherhood.
During pregnancy, estrogen and progesterone levels increase significantly to help support the development of the fetus and maintain the pregnancy. These hormones also play a role in preparing the breasts for lactation and the body for childbirth.
After childbirth, sex hormones continue to play a role in the postpartum period. For example, estrogen and progesterone levels decrease rapidly after delivery, which can contribute to postpartum mood changes and the “baby blues.” These hormone levels then gradually return to pre-pregnancy levels over the course of several weeks or months.
In addition to their effects on the reproductive system and mood, sex hormones can also have other effects on the body during motherhood. For example, estrogen can affect bone density, cardiovascular health, and skin health, while progesterone can affect sleep and metabolism.
It is important to note that various medical conditions and lifestyle factors can affect sex hormone levels, and it is important to speak with a healthcare provider if you have any concerns about your hormone levels during pregnancy or motherhood
At Precisionary Instruments, we’re thrilled to shine a spotlight on innovative labs around the world that are advancing science in unique and meaningful ways. This
Artificial Cerebrospinal Fluid (ACSF) is an essential buffer solution widely used in electrophysiology experiments, particularly to keep acute brain slices alive during research. This solution closely mimics the natural cerebrospinal fluid found in the brain and is designed to maintain neuronal viability and function during experiments like patch-clamp recordings. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of ACSF, its composition, and practical tips to optimize its use.
You’ll hear back from us in one business day
© 2023 Copyright
*Academic discounts are only valid for customers in North America.
© 2023 copyright